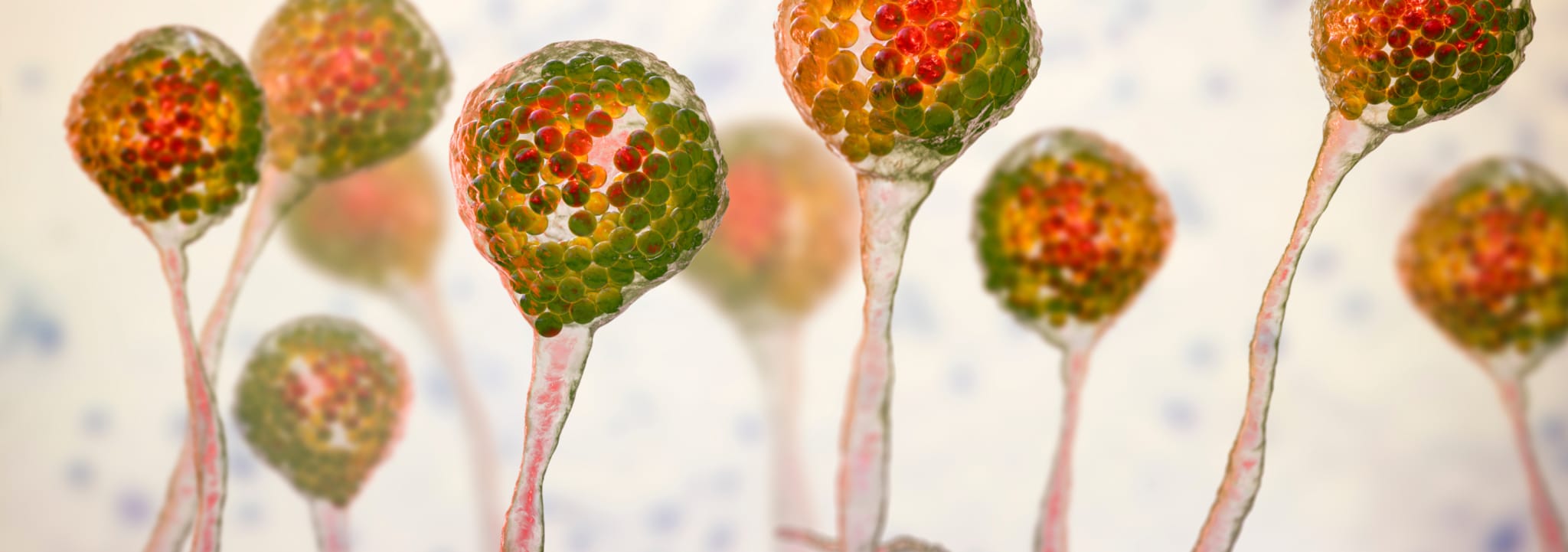
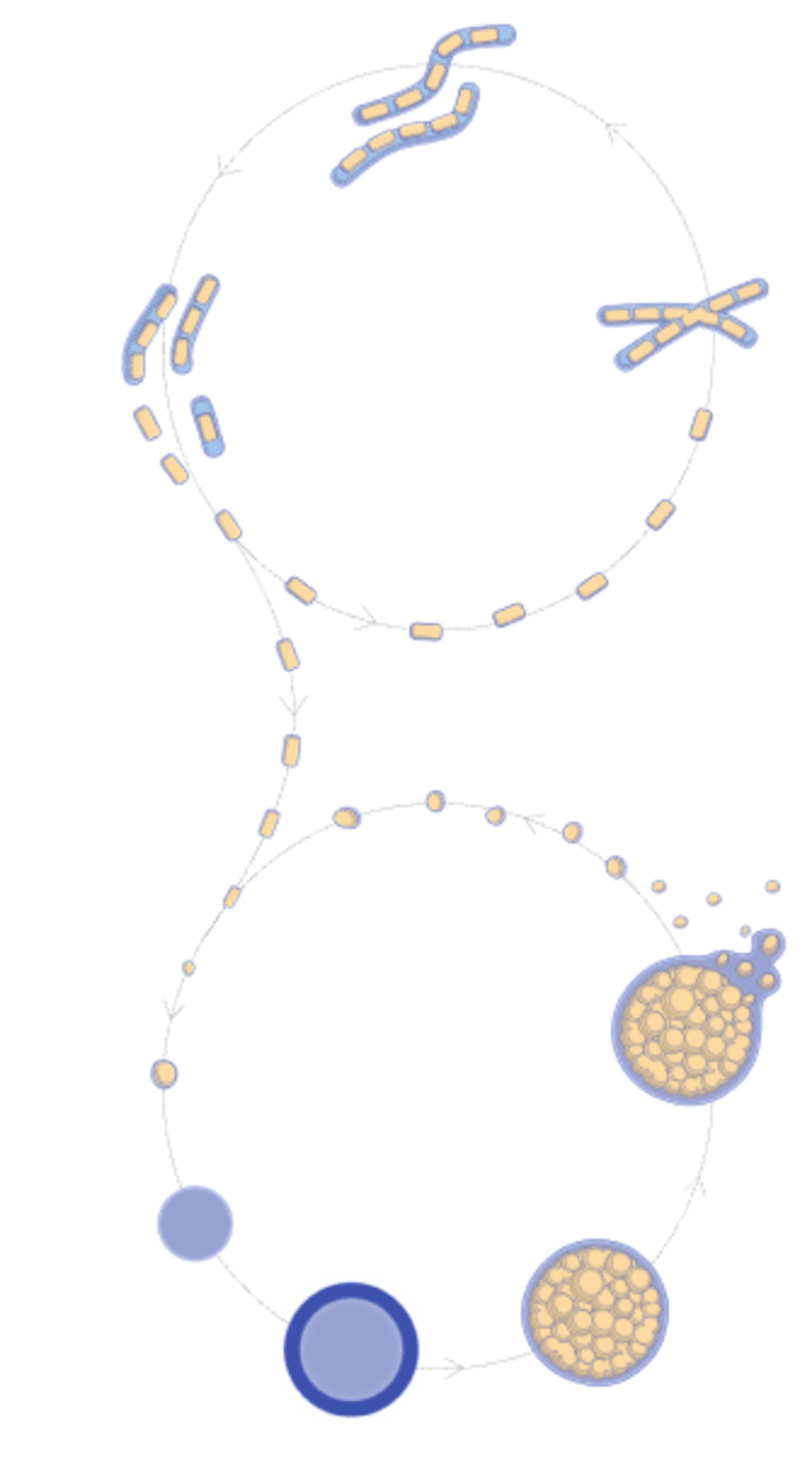
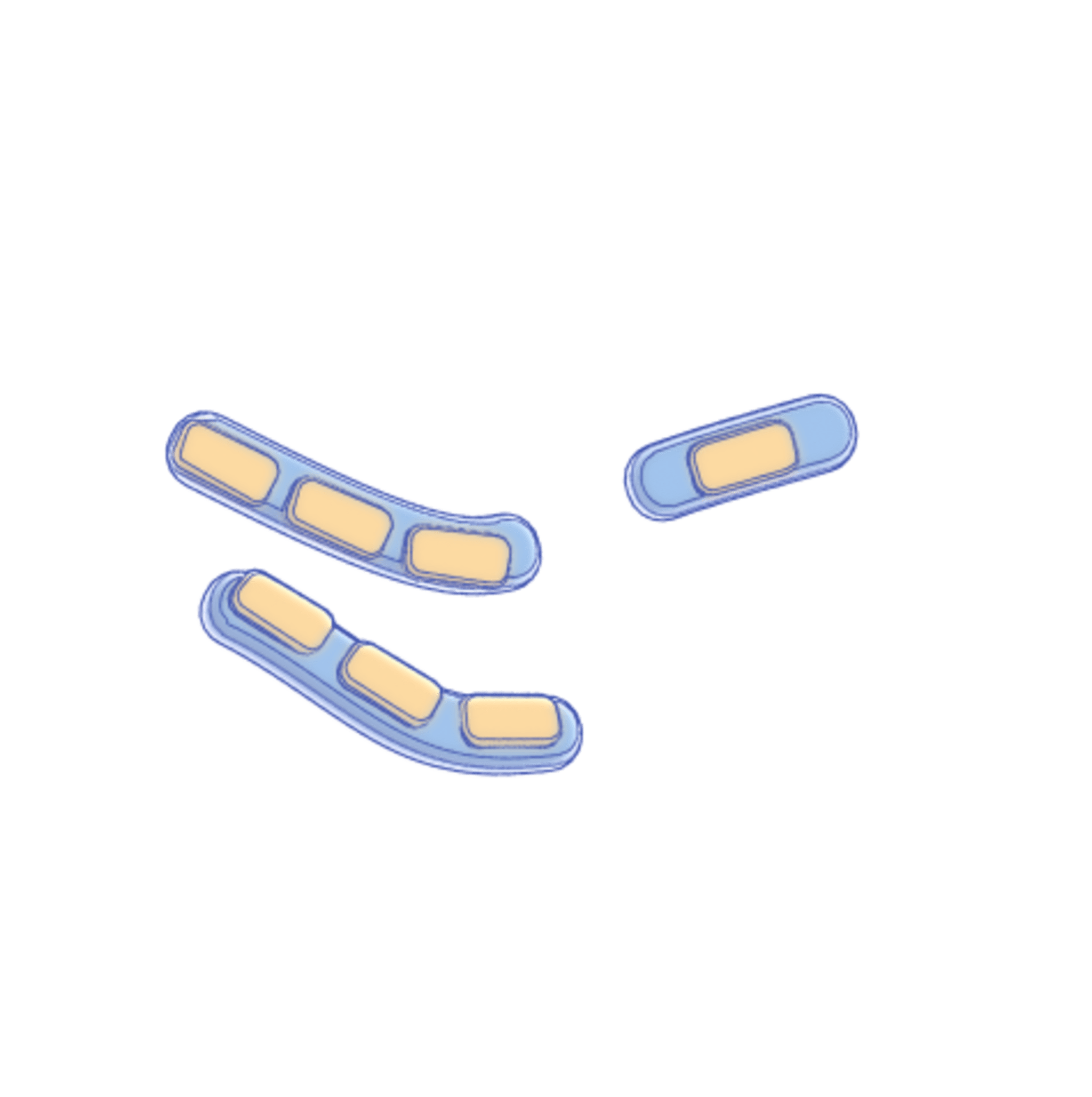
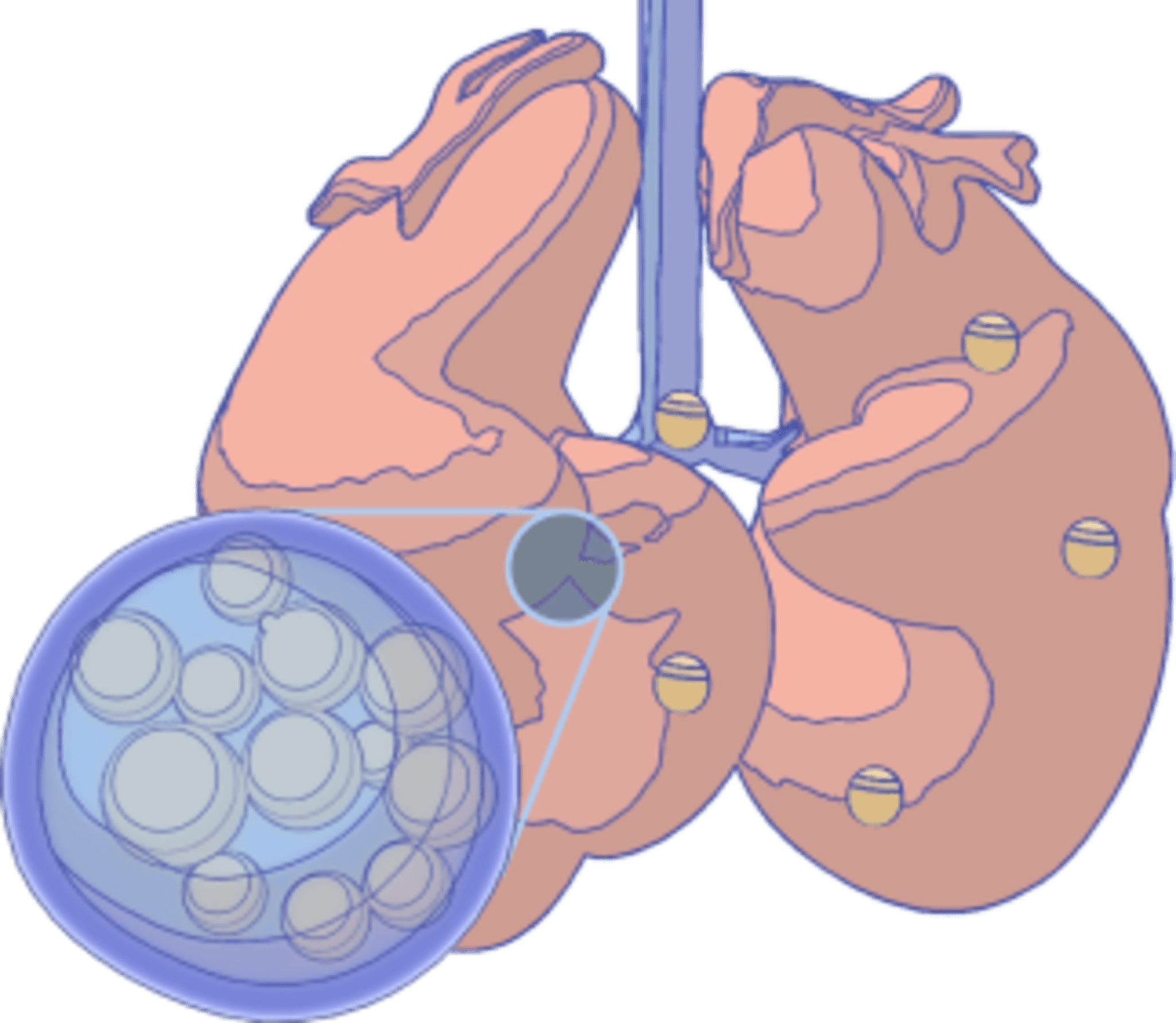
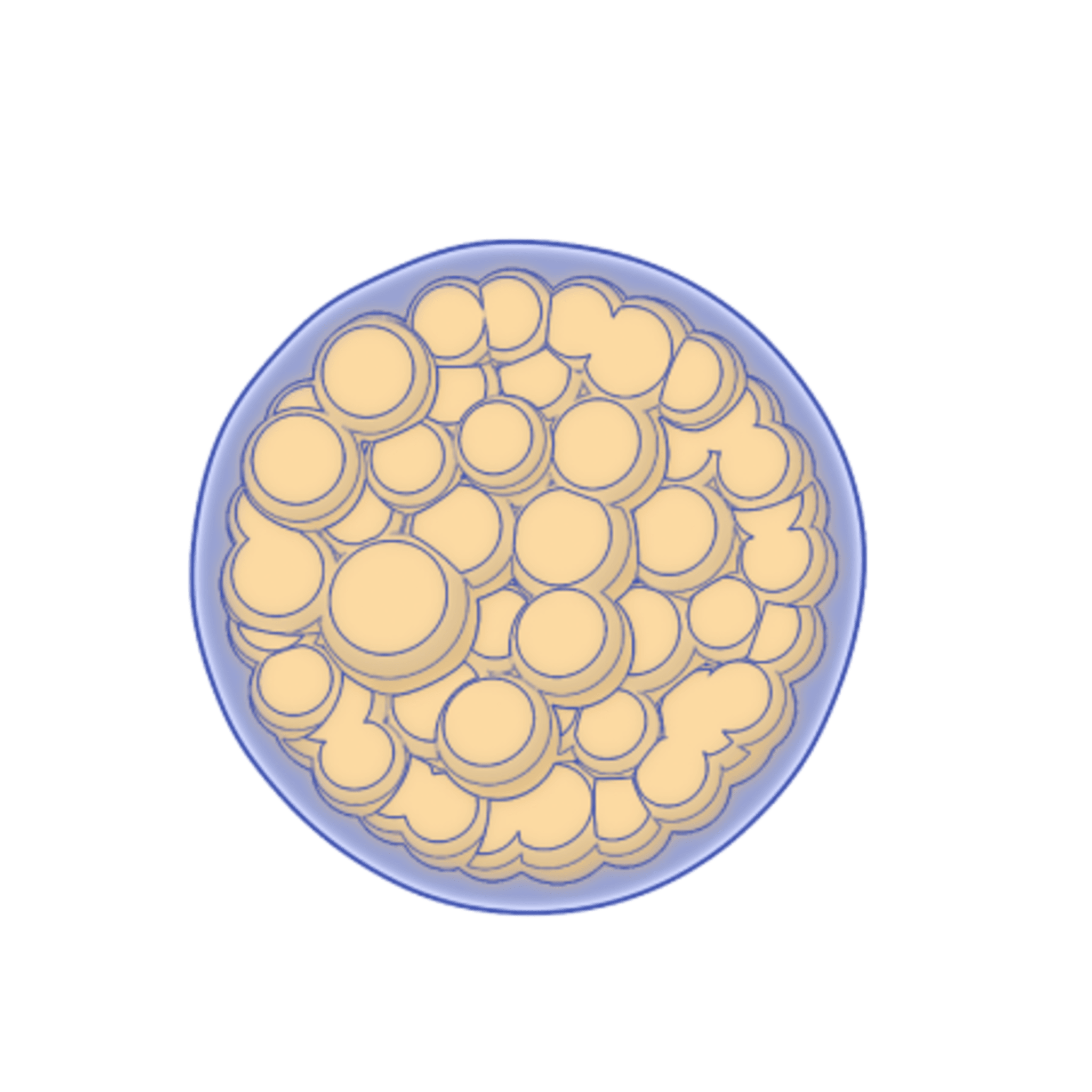
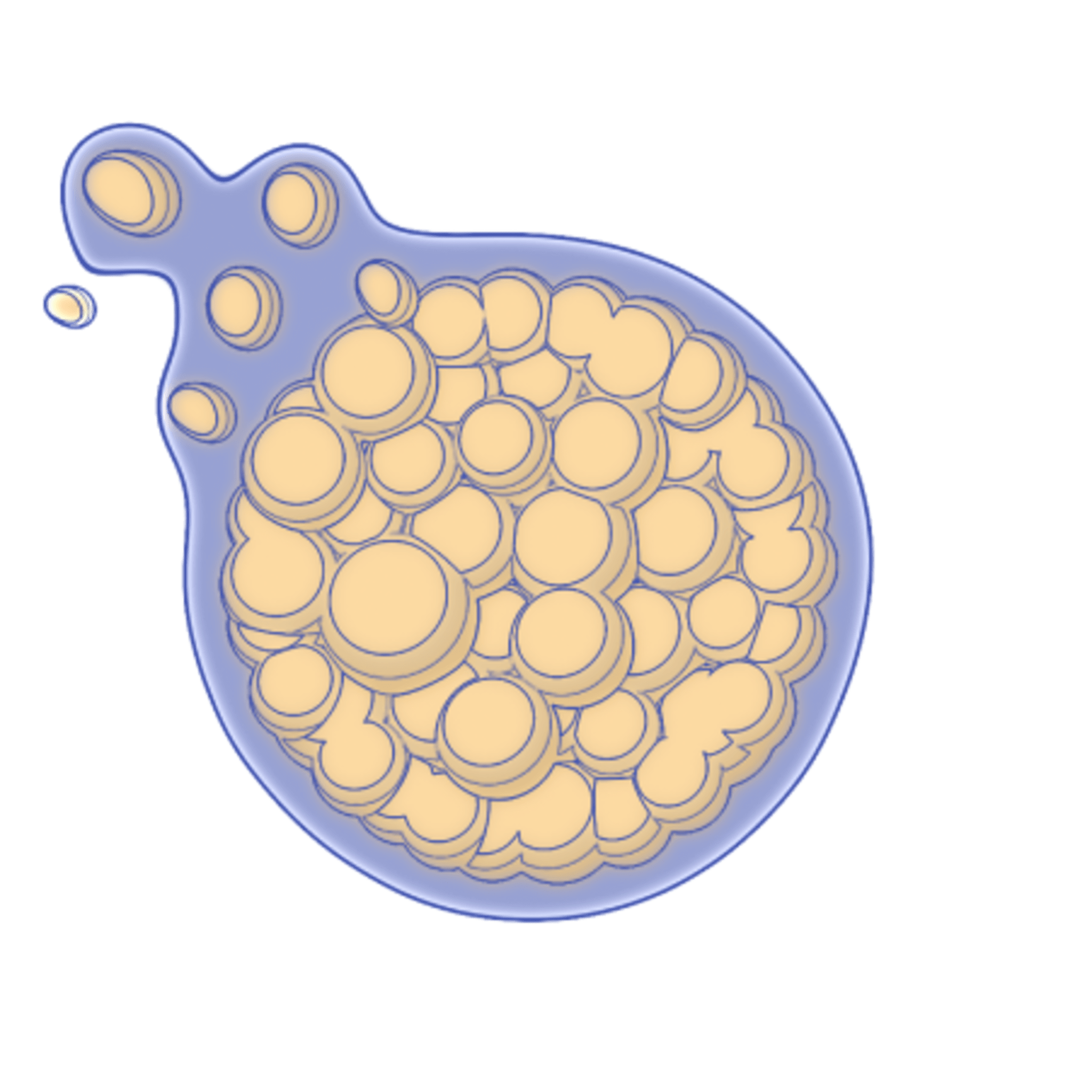
Coccidioides fungi are a type of soil-dwelling fungus that belong to the family Onygenaceae. They are known for their distinctive lifecycle and their ability to cause Valley Fever (coccidomycosis). Coccidioides fungi have a unique lifecycle that begins when the fungus grows as a filamentous mold in the soil. Under dry and dusty conditions, the fungus produces small, round structures called arthroconidia that can become airborne and be dispersed over large distances by wind. This dispersal mechanism allows Coccidioides fungi to colonize new areas and maintain their population in harsh environments.

While Coccidioides fungi are best known for their impact on human health, they also play an important ecological role in soil ecosystems. These fungi are decomposers, which means that they break down organic matter in the soil and recycle nutrients. This helps to maintain soil fertility and supports the growth of plants and other organisms.